

Your child's tolerance for specific medications, procedures, or therapiesĮxpectations for the course of the conditionĪntibiotic medication by mouth or ear drops Your child's age, overall health, and medical history Specific treatment for otitis media will be determined by your child's physician based on the following: This is a difficult test to perform in younger children because the child needs to remain still and not cry, talk, or move.Ī hearing test may be performed for children who have frequent ear infections. It does not tell if the child is hearing or not, but helps to detect any changes in pressure in the middle ear. Tympanometry, is a test that can be performed in most physicians' offices to help determine how the middle ear is functioning. A pneumatic otoscope blows a puff of air into the ear to test eardrum movement. The otoscope is a lighted instrument that allows the physician to see inside the ear. In addition to a complete medical history and physical examination, your child's physician will inspect the outer ear(s) and eardrum(s) using an otoscope. Always consult your child's physician for a diagnosis. The symptoms of otitis media may resemble other conditions or medical problems. However, each child may experience symptoms differently. The following are the most common symptoms of otitis media. May result in difficulty fighting new infection and hearing loss. Fluid remains in the middle ear for a prolonged period or returns again and again, even though there is no infection. The child may experience a feeling of fullness in the ear and hearing loss.Ĭhronic otitis media with effusion (COME). Otitis media with effusion (OME.) Fluid (effusion) and mucus continue to accumulate in the middle ear after an initial infection subsides. Fluid and mucus become trapped inside the ear, causing the child to have a fever, ear pain, and hearing loss. The middle ear infection occurs abruptly causing swelling and redness. What are the different types of otitis media?ĭifferent types of otitis media include the following:Īcute otitis media (AOM). The following are some of the reasons that the eustachian tube may not work properly:Ī cold or allergy which can lead to swelling and congestion of the lining of the nose, throat, and eustachian tube (this swelling prevents the normal flow of fluids)

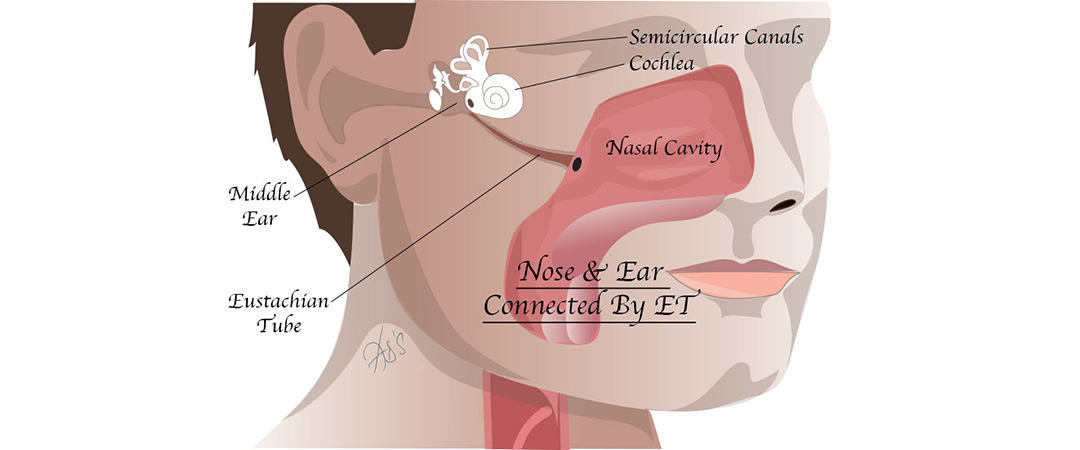
When this fluid cannot drain, it allows for the growth of bacteria and viruses in the ear that can lead to acute otitis media. When this tube is not working properly, it prevents normal drainage of fluid from the middle ear, causing a build up of fluid behind the eardrum. The eustachian tube helps to equalize the pressure between the outer ear and the middle ear. Middle ear infections are usually a result of a malfunction of the eustachian tube, a canal that links the middle ear with the throat area. While any child may develop an ear infection, the following are some of the factors that may increase your child's risk of developing ear infections:īottle-fed while laying on his or her back Who is at risk for getting ear infections? Otitis media can also affect adults, although it is primarily a condition that occurs in children. More than 80 percent of children have at least one episode of otitis media by the time they are 3 years of age. Otitis media can occur as a result of a cold, sore throat, or respiratory infection. Otitis media is inflammation located in the middle ear.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
